Decoding Foreign Financial Holdings: Significance and Advantages

The realm of finance extends beyond national boundaries, prompting many to investigate international banking. Grasping the concept of foreign financial holdings and their implications is crucial for those seeking to broaden their financial portfolio or manage their assets more efficiently.
In this article, we explore what constitutes a foreign financial holding, its advantages, how it contrasts with standard accounts, and the associated legal and tax considerations.
What Is a Foreign Financial Holding?
A foreign financial holding is a bank account maintained by a financial institution located outside the account holder’s country of residence.
Typically, these are situated in regions considered financial sanctuaries due to favorable banking regulations, political stability, and low or no taxation policies.
The concept of foreign financial holdings encompasses more than just storing funds in an overseas bank; it includes managing assets in a jurisdiction that offers financial advantages not available in one’s home country.
Advantages of Foreign Financial Holdings-
- Improved confidentiality
- Asset safeguarding
- Risk diversification
- Access to global financial services
- Suitable for managing wealth across borders
- Enables investment in international markets
- Shields assets from local economic instability
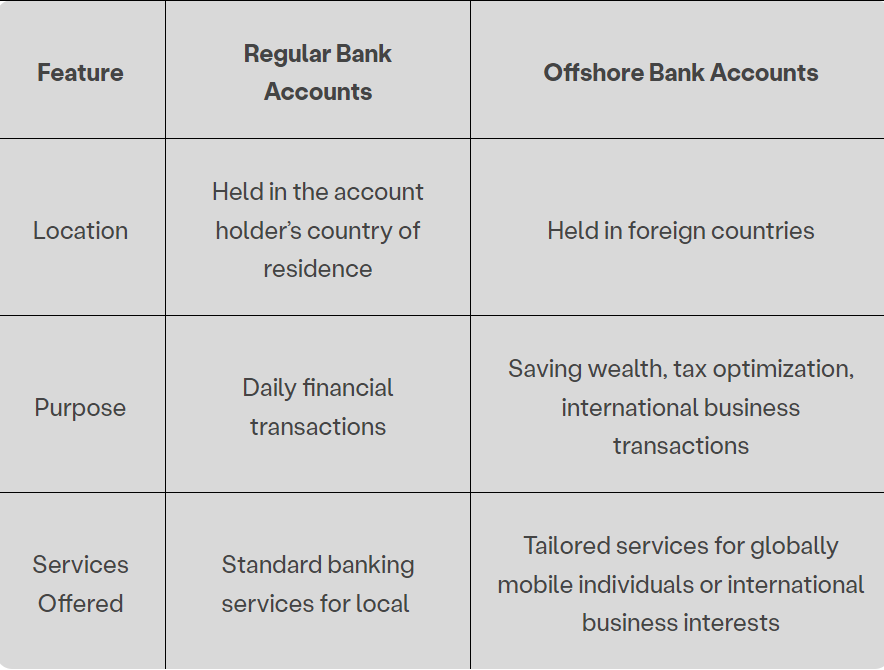
Differences between Standard Bank Accounts and Foreign Financial Holdings Feature-
Legal and Legitimate Uses of Foreign Financial Holdings –
Contrary to common misconceptions, foreign financial holdings are legal and legitimate financial tools. They are regulated by international financial standards, ensuring they are not used for illegal activities like money laundering or tax evasion.
Most countries require individuals to report their foreign financial holdings and their income, ensuring transparency and legal compliance.
Common Reasons for Opening a Foreign Financial Holding –
People open foreign financial holdings for various reasons, including the desire for increased financial privacy, protection against local political or economic instability, and the advantages of international diversification.
Businesses often use foreign financial holdings to facilitate international trade, manage currency risk, and capitalize on specific financial services that may not be available domestically.
Taxation of Foreign Financial Holdings-
The taxation of funds in a foreign financial holding depends on the account holder’s country of residence and its tax laws. Most countries tax their residents on worldwide income, which includes income generated from foreign financial holdings.
Account holders must declare their foreign income and pay taxes accordingly to avoid legal penalties.
Understanding how taxation works with foreign financial holdings is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring that all financial activities are conducted within legal boundaries.
Strategic Financial Planning with Foreign Financial Holdings-
Foreign financial holdings can be an integral part of strategic financial planning, especially for those with international financial needs or seeking enhanced asset management features.
These accounts allow for greater flexibility in terms of currency management, providing account holders with the ability to hold multiple currencies and mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations.
This is particularly advantageous for expatriates or businesses that operate across different countries, as it simplifies transactions and reduces exchange rate losses.
Leveraging Foreign Financial Holdings for Retirement Savings-
Additionally, foreign financial holdings can be used effectively for retirement planning. They offer access to international investment opportunities and funds that might not be available in the account holder’s home country.
By diversifying retirement savings across different jurisdictions, one can protect retirement funds from potential country-specific economic downturns or fiscal instabilities. This level of diversification is critical in building a resilient retirement portfolio that can withstand various economic conditions.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the concept of foreign financial holdings opens up a world of opportunities for effective financial management and international investment.
While foreign financial holdings offer significant benefits, they also require careful consideration of legal and tax obligations to ensure they serve their purpose without complicating the account holder’s financial affairs.
FAQs’
Q1. What are the advantages of having a foreign financial holding?
Ans- The advantages of having a foreign financial holding include greater privacy, favorable banking conditions like low or no taxation, protection against local political or economic instability, and access to specialized financial services. Additionally, these accounts can facilitate international business operations and help manage currency fluctuations.
Q2. How does a foreign financial holding differ from a standard bank account?
Ans- A foreign financial holding is typically located in a jurisdiction outside the account holder’s country of residence. It offers benefits like tax optimization, privacy, and asset protection. These accounts are favored for international financial transactions and investment purposes rather than daily banking needs, which distinguishes them from standard bank accounts.
Q3. Are foreign financial holdings legal and legitimate?
Ans- Yes, foreign financial holdings are legal and legitimate, provided they are used in compliance with the tax laws and regulations of the account holder’s country of residence. They are subject to international banking regulations that aim to prevent illegal activities such as tax evasion and money laundering.
Q4. What are some common reasons for opening a foreign financial holding?
Ans- Common reasons for opening a foreign financial holding include seeking financial privacy, protecting assets from lawsuits or claims, benefiting from tax efficiency, diversifying investments internationally, and facilitating business transactions across borders.
Q5. How does taxation work for funds held in a foreign financial holding?
Ans- Taxation for funds held in a foreign financial holding typically requires the account holders to report income generated from these accounts to their home country’s tax authorities. Most countries tax global income, so declaring foreign income and paying appropriate taxes is essential to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Q6. Can I open a foreign financial holding account without visiting the country?
Ans- Yes, you can often open a foreign financial holding account remotely. Many international banks allow you to set up an account online, although some may require you to submit notarized documents or visit a local branch.
Q7. What risks come with foreign financial holdings?
Ans- While foreign financial holdings offer benefits, they also come with risks like changes in the host country’s banking rules, currency fluctuations, political instability, and the complexity of managing taxes across different countries.
Q8. Can foreign financial holdings help with estate planning?
Ans- Yes, foreign financial holdings can be useful for estate planning. They help diversify assets, protect wealth from local inheritance laws, and may offer better conditions for passing on wealth to heirs, depending on the country’s regulations.
Q9. How can I keep my funds safe in a foreign financial holding?
Ans- To keep your funds safe in a foreign financial holding, choose reputable banks in stable countries with strong financial regulations. Consider the bank’s financial health, deposit protection schemes, and the legal framework of the country where the account is held.
Q10. What are the rules for reporting foreign financial holdings?
Ans- Reporting rules for foreign financial holdings vary by country. Most countries require you to report your foreign accounts and any income earned to tax authorities. Failing to report these accounts can result in heavy penalties, so it’s important to know your country’s specific rules.



