How to Open an SBI NRE Account as an NRI?

For Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) with financial ties to India, understanding NRE accounts is crucial. This post explores NRE accounts, their benefits, drawbacks, and tax implications offered by SBI.
What is an NRE Account?
An NRE account, a Non-Resident External account, is a rupee-denominated savings account tailored for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) residing outside India. This specialized account enables NRIs to deposit and oversee their income earned from abroad, offering them a convenient avenue for managing their finances while living outside the country.
Benefits of NRE Accounts:
- NRE accounts allow NRIs to deposit foreign earnings converted to rupees at the prevailing exchange rate.
- The principal amount and interest earned in NRE accounts are generally exempt from Indian income tax.
- Funds in NRE accounts can be freely repatriated abroad without restrictions, facilitating the easy transfer of money back outside of India.
- NRE account holders can utilize their funds for various investments in India, subject to regulations outlined in the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Disadvantages of NRE Accounts:
- Lower Interest Rates: NRE accounts generally feature lower interest rates when compared to NRO accounts or resident savings accounts in India.
- Limited Account Usage: Funds held in NRE accounts cannot be directly used for regular living expenses in India. An NRO account is necessary for such purposes.
Tax Implications of NRE Accounts:
- Interest Income: Generally, interest earned on NRE accounts is exempt from Indian income tax. However, the interest income earned on your NRE account might be taxable in your country of residence. Many countries have taxation worldwide, meaning they tax income earned anywhere globally. Many countries have DTAAs with India to avoid double taxation on the same income. Suppose your resident country has a DTAA with India. In that case, the DTAA might reduce or eliminate the tax on your NRE interest income in your resident country. It’s always advisable to consult a tax advisor for the latest tax regulations and any potential implications based on your situation and tax residency status. You can also research the DTAA between India and your resident country to understand its provisions on taxing interest income earned on NRE accounts.
Features of NRE Accounts for SBI Bank
NRE accounts offer a range of features, including SMS Alerts, Multi-City Cheque Book (MCC), International or Domestic Debit Cards, and Internet banking services. They serve as a platform to park overseas earnings remitted to India and converted to Indian Rupees. These accounts can be opened individually or jointly with other NRIs / PIOs / OCIs and support various types, including Savings Bank, Current Account, Term Deposit, Special Term Deposit, and Recurring Deposit. Funds deposited in NRE accounts can originate from fresh remittances from overseas or transfers from other NRE / NRO / FCNR (B) accounts. Moreover, account holders can open accounts with close resident relatives on a “former or survivor” basis. They can withdraw funds to make local payments in Rupees. Importantly, interest earned on NRE accounts is exempt from Indian income tax, and individuals can take advantage of rupee loans against NRE deposits. The tenor Of Deposits (TDR/STDR/RD) ranges from a minimum period of 1 year to a maximum of 10 years, with the interest income being exempted from Indian income tax.
Eligibility Criteria to open an NRE Account in SBI
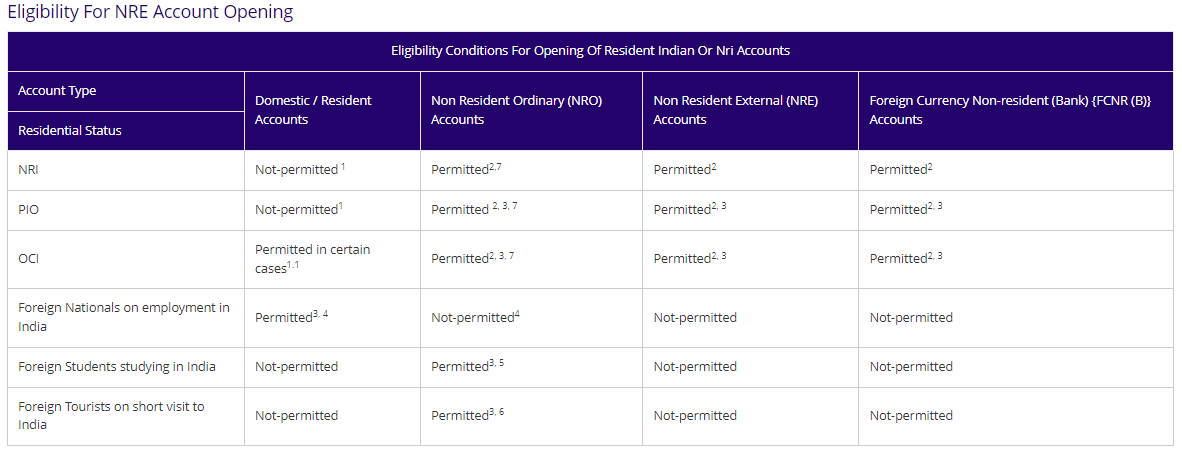
(Source: https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/non-residential-external)
Who can open an NRE account?
(2) NRIs can open a joint account with a Resident Indian (RI) who is a close relative subject to the following conditions:
- The permitted operation mode is ‘Former (NRI) or Survivor’ only.
- The NRI (PIO / OCI) will be the joint account’s primary/first account holder, and RI will be the second applicant.
- Non-resident individuals, including NRIs/PIOs/OCIs, can establish and maintain joint NRE accounts with resident relatives on a “Former or Survivor” basis. The eligible relationships for joint accounts include:
- Members of a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- Husband and wife
- Individuals related to each other in a prescribed manner, including:
- Father (includes step-father)
- Mother (includes step-mother)
- Son (includes step-son)
- Son’s wife
- Daughter
- Daughter’s husband
- Brother (includes step-brother)
- Sister (includes step-sister)
(3) Following conditions applicable:
- Pakistani nationals will require prior approval from RBI before opening the account.
- Bangladesh National to have a valid visa and residential permit issued by the Foreigner Registration Office (FRO) / Foreigner Regional Registration Office (FRRO) concerned.
Permissible credits
- Transfer from another NRE / FCNR (B) account.
- Transfer from another NRO account is subject to specific limits.
- Fresh remittance from abroad through the banking channel.
- Personal cheques drawn on a foreign account.
- Proceeds of Foreign Currency Notes / Travelers cheques tendered by NRI / PIO / OCI while visiting India, with amounts exceeding USD 5000 (or equivalent) in currency or USD 10,000/- (or equivalent) in Travelers cheques requiring a Currency Declaration Form.
- Drafts issued by banks/exchange companies abroad.
- Interest, dividend, and maturity proceeds of investments made in India are subject to repatriable basis.
- Interest Rates
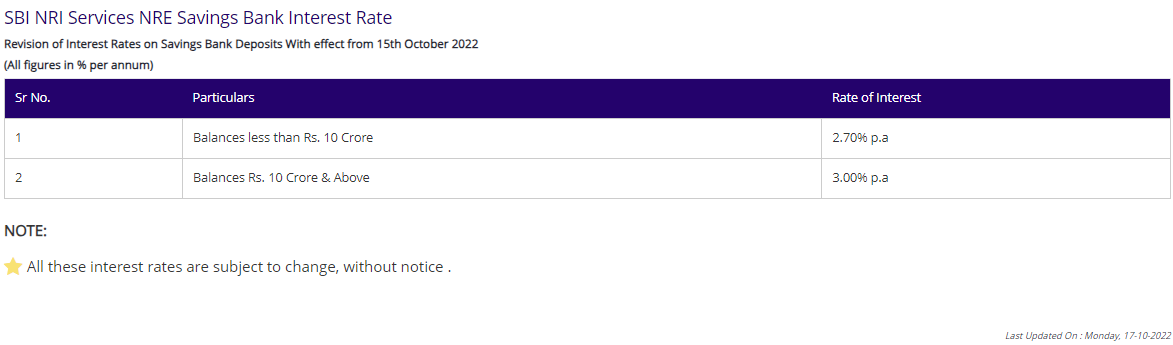
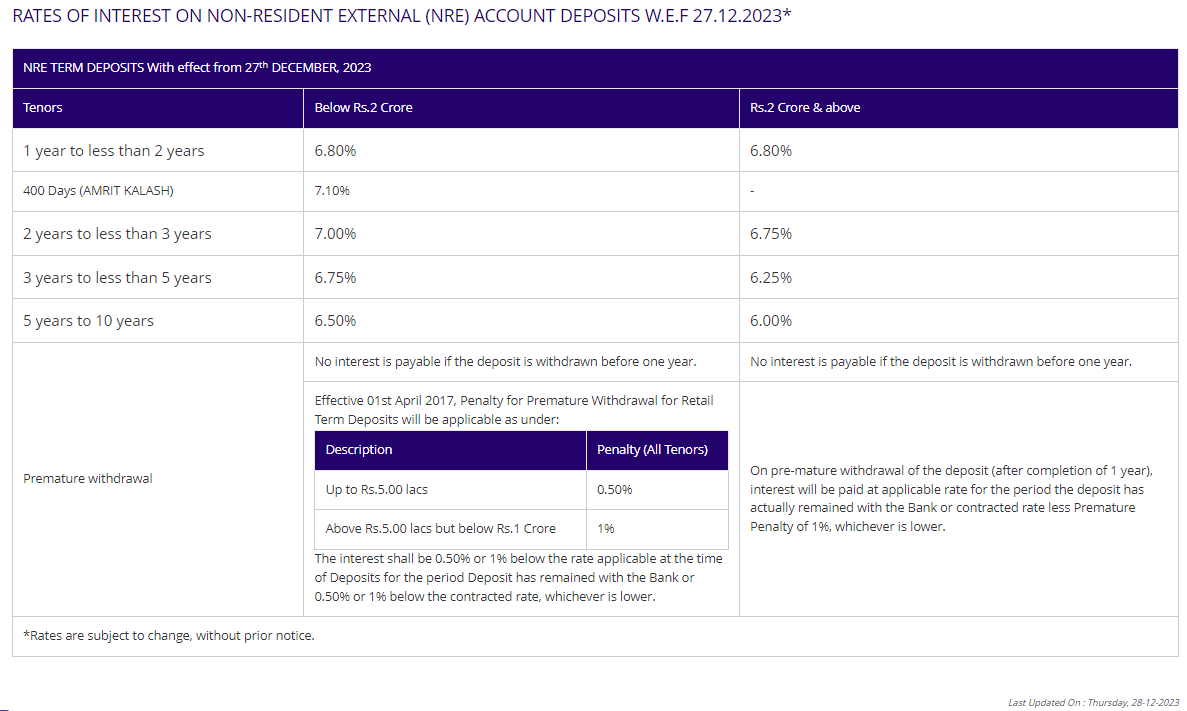
Types of NRE Accounts
These encompass various options tailored to the needs of Non-Resident Indians (NRIs). These include Savings Bank (SB) / Current Account, Term Deposits (TDR), Recurring Deposits (RD), and Special Term Deposits (STDR).
- NRE Savings Bank or Current Accounts are rupee-denominated and can be initiated without an initial balance. However, it’s advisable to fund the account promptly to evade charges for non-maintenance of the Minimum Average Balance. While interest is paid quarterly on the daily balance in Savings Bank accounts, no interest is accrued in Current Accounts. The minimum deposit requirements vary based on the branch type, with repatriation of principal and interest amounts permissible. Additionally, nomination facilities are available for account holders.
- Term Deposits (TDR) provide NRIs with fixed tenure rupee deposits, offering flexibility in deposit amounts and tenure. Interest is paid quarterly and can be credited to the NRE Savings Bank account upon request. Like Savings Bank accounts, minimum deposit requirements differ by branch type, with full repatriability of principal and interest amounts. These deposits also offer loan and overdraft facilities, premature withdrawal options, and automatic renewal upon maturity.
- Recurring Deposits (RD) systematically cater to those seeking to save for future financial goals. With a minimum monthly installment requirement, these deposits allow principal and interest amounts to be fully repatriable. Like other NRE accounts, RDs offer nomination facilities, loan and overdraft options, and premature withdrawal allowances.
- Particular Term Deposits (STDR) provide a fixed tenure rupee deposit option with compounded interest, paid with the principal upon maturity. They share similarities with TDRs regarding deposit requirements, repatriation options, nomination facilities, loan and overdraft availability, premature withdrawal permissions, and automatic renewal features.
- NRE Non-Callable Term Deposit Account is available for one year and two years, with a minimum deposit of Rs. 1,00,01,000 (One Crore and one thousand) and above. There is no maximum limit on the deposit amount. Interest rates are subject to change and can be checked for the latest rates. Interest on Term Deposits is paid monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, or yearly. At the same time, Special Term Deposits accrue interest and are paid out on maturity. Premature withdrawal is generally not permitted except in cases of deceased settlement or under the direction of relevant authorities, with approval from branch controllers. In exceptional circumstances, premature withdrawal may be allowed with Branch controllers’ approval. However, no interest will be paid in such cases. Upon maturity, the account is automatically renewed into a regular NRE Term Deposit for the same duration. A loan facility is also available against Term Deposits, with repayment aligned with the remaining deposit period.
- NRE Salary Account is designed to deposit monthly overseas earnings in Indian rupees. It can be opened individually or jointly with other NRIs / PIOs / OCIs. It functions as a Savings Bank account, with funds deposited as fresh remittances from overseas or transfers from other NRE / NRO / FCNR (B) accounts. Notably, interest earned on NRE accounts is exempt from Indian Income tax. Additionally, there are various benefits associated with NRI Home and Car loans, including waivers on service charges. These waivers cover SMS alerts, NEFT / RTGS transactions, issuance of multi-city cheque books and demand drafts, debit card annual maintenance, PIS account opening, and 50% of NRI Home Loan processing charges. Moreover, specific requirements for availing NRI Car Loans are waived if the NRE salary account is at least three months old with continuous salary credit or if the account has been maintained for at least twelve months with a minimum average balance of Rs. 50,000/- or an initial deposit of USD 5000/- or equivalent. Eligibility criteria depend on whether the account holder is working for an Indian or overseas employer, with additional documentation required for KYC compliance, such as a salary slip, employee identity card, or letter from the employer’s HR/Admin department.
NRI ‘Sukoon’ Current Account is tailored for NRIs seeking a rupee-denominated account without interest accrual. It can be initiated with a zero balance. However, funding upfront is advised to circumvent charges for non-maintenance of the Minimum Average Balance (AMB), which stands at Rs. 3,000/-. The balance is fully repatriable, and the account offers a nomination facility. Notably, no interest is paid on Current Accounts. It facilitates funds transfer to any overseas account. It is ideal for NRIs who prefer to avoid earning interest due to personal reasons. The account accepts funds as fresh remittances from overseas or transfers from other NRE / FCNR (B) accounts.
- Additionally, it permits joint accounts with resident relatives on a “former or survivor” basis, extending to members of a Hindu Undivided Family, spouses, and other specified relationships. Permissible credits include various forms of remittance from abroad, personal cheques, foreign currency proceeds, drafts, and investment-related returns on a repatriable basis. Moreover, the account offers SMS alerts, a multi-city cheque book, international or domestic debit cards, internet banking, and an NRI Family Card.
Premature withdrawals
Premature withdrawals from term deposits entail specific penalties and conditions. For deposits below Rs.1 Crore, no interest is payable if the withdrawal occurs before one year. Effective April 1st, 2017, the penalty for premature withdrawal for retail term deposits up to Rs.5.00 lacs is set at 0.50% for all tenors. For deposits exceeding Rs.5.00 lacs but below Rs.1 Crore, the penalty is 1% across all tenors. The interest penalty is calculated at 0.50% or 1% below the applicable rate at the time of deposit or 0.50% or 1% below the contracted rate, whichever is lower. For withdrawals exceeding Rs.1 Crore, no interest is accrued if the withdrawal occurs before one year.
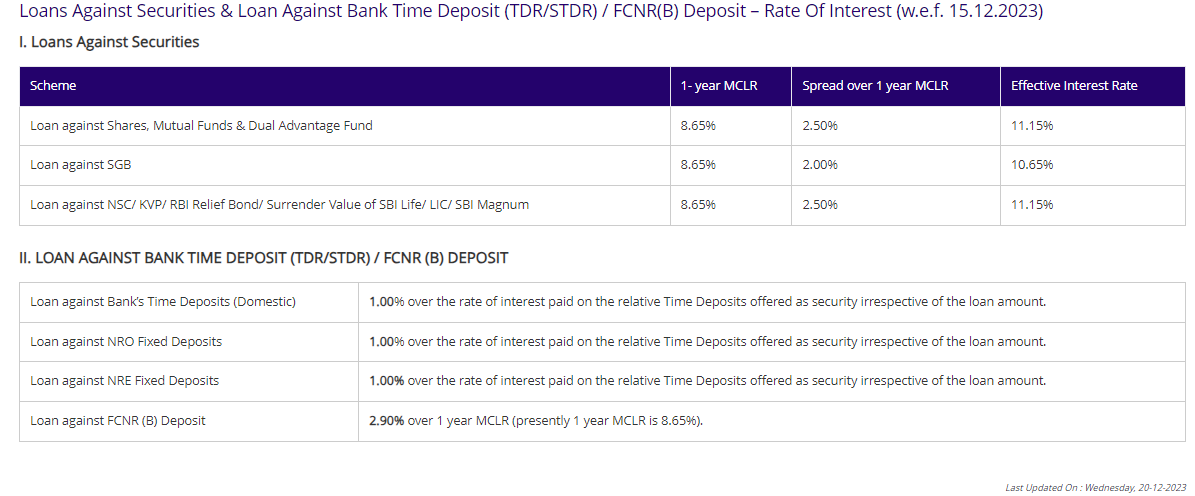
Loans against NRE deposits
NRE deposits serve as collateral for obtaining loans in Indian rupees. These loans can be utilized for various purposes, such as meeting emergency financial needs, conducting business activities, investing directly in India, or acquiring property in India. Notably, there’s no requirement to close the deposit prematurely to avail of the loan. Loans can be obtained directly at the branch where the deposit is maintained, either as an overdraft or as a demand loan. The maximum loan amount is typically up to 90% of the face value of the deposit, including the interest accrued. Interest rates on these loans are usually set at 1.00% over the rate paid on the corresponding deposit used as security.
Funds Transfer From NRE To Overseas Account
Transferring funds from your NRE Savings Bank account or deposits to overseas accounts is straightforward, allowing for full repatriation of funds. Through Internet Banking (INB), you can initiate outward remittances or funds transfer requests favouring yourself or third parties. This can be done from your NRE Savings Bank account, NRE fixed deposit account, or FCNR (B) account holders to any overseas account. To begin, you’ll need to add a beneficiary and then submit a request for remittance in their favour. Once a beneficiary is added, their details are stored in the system, allowing you to send multiple remittances to them at any time. Adding a beneficiary involves:
- Logging into your INB account.
- Navigating to the profile tab.
- Following the steps outlined for managing beneficiaries.
After adding a beneficiary, you can place a remittance request by logging into your INB account, clicking on the payments/transfers tab, and selecting the option for international funds transfer. From there, you can enter the details for the transfer and proceed accordingly.
Alternatively, suppose you prefer to initiate the transfer through a branch. You can download a standard request letter from the bank’s website under the “Download Forms” section (https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/download-forms). This letter is for outward remittance from NRE/FCNR (B) accounts. Once downloaded, you can complete the required information and submit the letter to your home branch via post or courier. It’s important to note that requests sent via email cannot be processed for security reasons, so it’s advisable to use the designated standard request letter for branch transactions.
Procedure to open an NRE account in SBI
- Online Application: Click on the provided link to fill out the online account opening application. Follow the process outlined to complete the application digitally. (https://oaa.onlinesbi.sbi/oaonri/onlineaccapp.htm)
- Offline Application: Alternatively, you can download the account opening application by clicking on the provided link. Fill out the form manually and gather the necessary documents for KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements. Once completed, send the application and the attested copies of the required proofs and documents to your preferred home branch in India. (https://sbi.co.in/documents/21077/23246/SBI_NRI_Account_Opening_Application.pdf)
- Visit a Branch: Another option is to visit an SBI branch in India or overseas. Please fill out the application form provided at the branch and submit it along with the required proofs and documents for KYC verification.
A financial advisor can provide valuable insights tailored to an individual’s specific financial circumstances and goals. They help navigate through the varied investment opportunities and currency options available within FCNR accounts, ensuring compliance with both Indian and international tax laws. Moreover, advisors can offer strategic guidance on how to maximize returns and minimize financial risks, making the process of managing foreign currency assets more effective and streamlined. Reach out to us at office@primewealth.co.in
This blog is for informational purposes only. The information here does not represent legal advice and should not be used as such. Please confirm the accuracy of any data or content from reliable sources on your own.



