How to Open an SBI NRO Account as an NRI?

For Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) with financial ties to India, understanding NRO accounts is crucial. This post explores NRO accounts, their benefits, drawbacks, and tax implications as offered by SBI.
What is an NRO Account?
An NRO account is a rupee-denominated savings account in India specifically designed for NRIs. It allows them to deposit and manage income earned in India, such as rent from property, pension payments, or interest on investments. Unlike NRE accounts (funded with foreign currency), funds in NRO accounts cannot be freely repatriated abroad.
Benefits of NRO Accounts:
- Convenience: NRIs can manage their Indian income efficiently in a rupee-denominated account.
- Investment Opportunities: Funds in NRO accounts can be used for various investments in India, like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds (subject to FEMA regulations).
- Expense Management: NRIs can utilize their NRO account to pay for living expenses of dependents in India, property taxes, or other local bills.
Disadvantages of NRO Accounts:
- Limited Repatriation: Repatriating funds from an NRO account is subject to limitations. Generally, only up to USD 1 million per financial year can be repatriated, and tax clearances may be required.
- Tax Implications: According to the NRI’s tax bracket, interest earned on NRO accounts is taxable in India. NRIs should consult a tax advisor to understand their specific tax obligations.
Tax Implications of NRO Accounts:
- Interest income earned on NRO accounts is subject to tax deducted at source (TDS) in India at a rate of 30% (subject to change). However, NRIs can claim a tax refund if the applicable tax rate in their country of residence is lower through a Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and their resident country.
- Capital gains earned from selling assets held in India through an NRO account may also be taxable in India.
Features of SBI NRO Account
SBI offers NRO accounts for NRIs (Non-Resident Indians) and PIOs (Persons of Indian Origin) to manage their Indian income in rupees. These accounts come with various features like SMS alerts, multi-city cheque books, debit cards, and Internet banking. They can be opened individually, jointly with other NRIs/PIOs/OCIs, or even with Resident Indians (on a “former or survivor” basis).
The account allows deposits from NRE/NRO/FCNR accounts or fresh remittances abroad. Funds can be withdrawn for local payments and used for investments subject to regulations. Interest earned is taxable (with potential tax treaty benefits), and rupee loans can be made available against NRO deposits. The account offers various deposit options like savings, current accounts, term deposits, and recurring deposits with varying interest rates based on deposit amount and tenure. There are penalties for premature withdrawals.
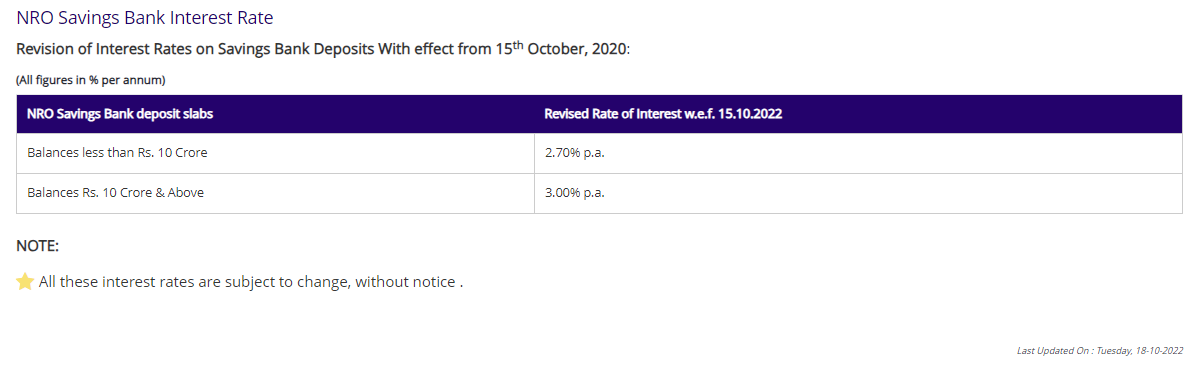
NRO Savings Bank Interest Rate
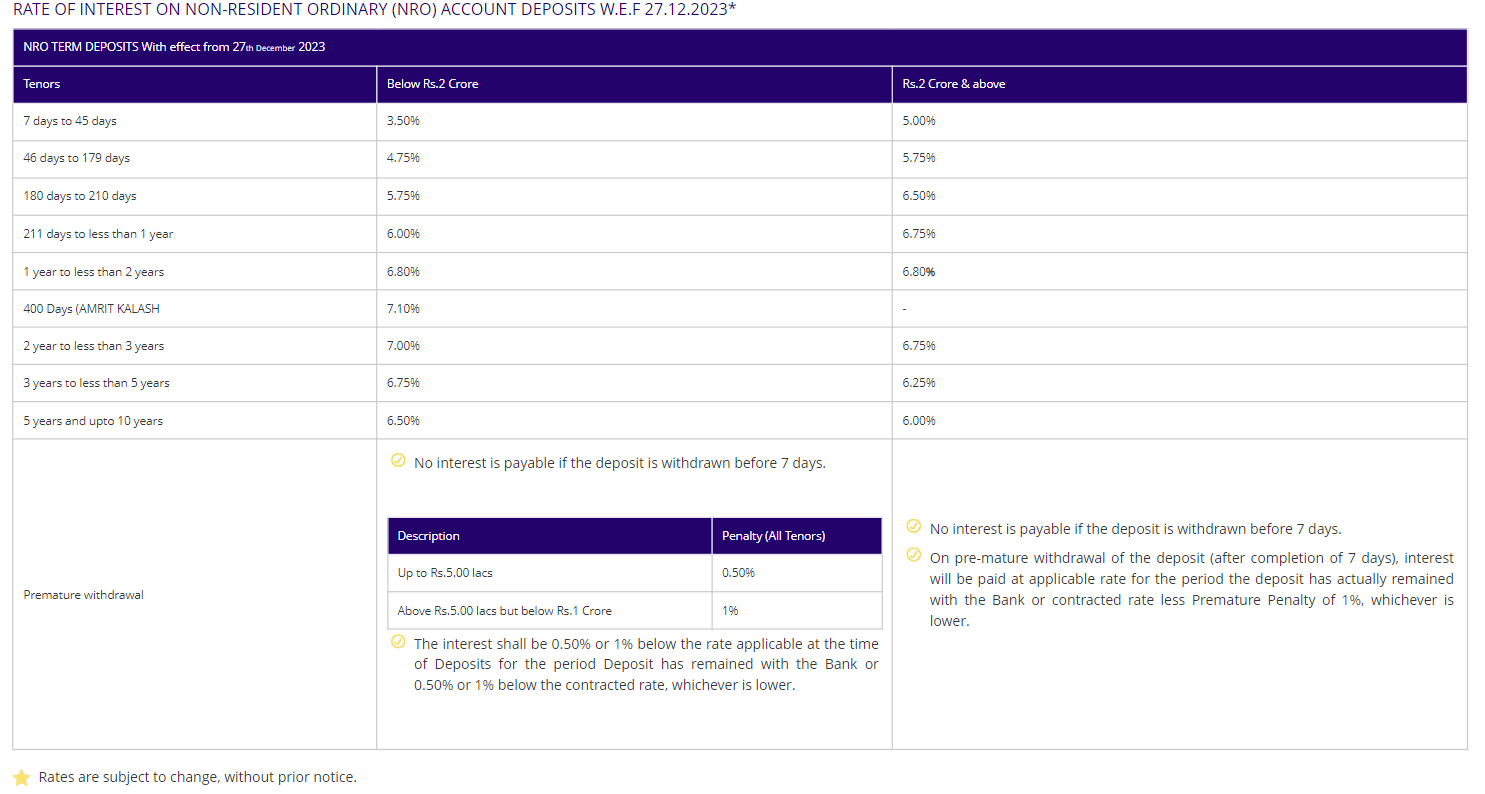
NRO Deposits (TDR / STDR / RD) Interest Rates
Eligibility for NRO Account Opening
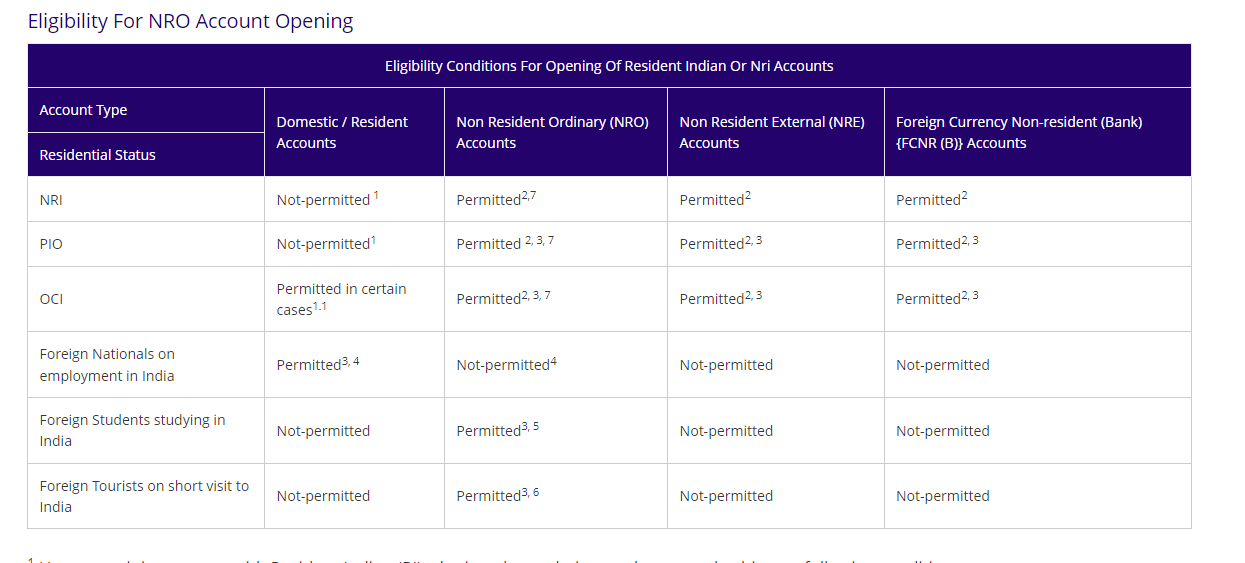
(Source: https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/nro-account#show)
Who can open a joint NRO account with a Resident Indian (RI)?
- Close relatives only: You can only open a joint NRO account with an RI who is a close relative.
- Two account structures: There are two ways to set up the account, depending on who you want to be the primary account holder:
- (1) RI as primary account holder: In this case, the account operates on an “Either or Survivor” basis. This means either the NRI or the RI can access the funds, and if one account holder dies, the other becomes the sole owner.
- (2) NRI as primary account holder: Here, the account operates on a “Former (NRI) or Survivor” basis. The NRI has primary access, but if the NRI dies, the RI becomes the sole owner. NRI/PIO/OCI individuals have the authorization to open and maintain their NRO accounts jointly with their Resident relative(s), provided the account operates on a “Former or Survivor” basis, with the NRI/PIO/OCI individual as the former account holder. The permissible joint holders include:
- Members of a Hindu Undivided Family
- Husband and wife
- Individuals related to each other as prescribed, such as:
- Father (including step-father)
- Mother (including step-mother)
- Son (including step-son)
- Son’s wife
- Daughter
- Daughter’s husband
- Brother (including step-brother)
- Sister (including step-sister)
- This arrangement allows NRI/PIO/OCI individuals to have resident relatives as joint holders on their NRO accounts for ease of operation and management.
Additional requirements for specific nationalities:
- (3) Pakistani nationals Need prior approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to open an account.
- (4) Bangladeshi nationals Must have a valid visa and residential permit.
(5) Special considerations for international students:
- Students can open NRO accounts with limited functionality for the first 30 days.
- During this period, they can only receive foreign remittances up to USD 1,000 and withdraw a maximum of Rs. 50,000 per month.
- To remove these limitations, students must provide proof of a valid local address within 30 days.
Important notes:
- (7) NRIs (including PIO / OCI) living in Nepal or Bhutan are prohibited from establishing an NRO account.
- (4, 6) Foreign nationals who convert their domestic accounts to NRO accounts after leaving India need RBI approval to continue using the account beyond six months.
Permissible credits for an account include:
- Transfers from another Resident Indian, NRE (Non-Resident External), or FCNR (Foreign Currency Non-Resident) account.
- Transfers from another NRO (Non-Resident Ordinary) account, specifically for paying legitimate dues in India.
- Fresh remittances from abroad through the banking channel.
- Personal cheques drawn on a foreign account.
- Proceeds of Foreign Currency Notes or traveler cheques tendered by NRI (Non-Resident Indian), PIO (Person of Indian Origin), or OCI (Overseas Citizen of India) while visiting India. However, any amounts surpassing USD 5000 (or its equivalent) in currency or USD 10,000 (or its equivalent) in Travelers’ cheques must be accompanied by a Currency Declaration Form. Additionally, interest, dividends, and maturity proceeds derived from investments made in India on a non-repatriable basis are included.
NRO Accounts: Savings Options and Repatriation Limits
Account Types:
- Savings Bank (SB) / Current Account: The Rupee-denominated account offers the flexibility of being opened with a zero balance. However, ensuring sufficient funding upfront is advisable to avoid charges for failing to maintain the Minimum Average Balance (MAB). Interest accrues quarterly on the daily balance within the Savings Bank account. In contrast, no interest is earned in the Current Account. Minimum deposit requirements vary depending on the branch type, with general branches following MAB criteria and personal banking branches mandating a minimum total customer account or deposit balance, differing for metro/urban and semi-urban/rural areas. Balances in these accounts are partly repatriable, subject to an overall ceiling of USD 1 million or equivalent in a financial year, and nomination facilities are available for account holders.
- Term Deposits (TDR): Rupee deposits with fixed tenures are offered, where interest is paid quarterly on Term Deposit Receipts (TDRs), and upon request, it can be credited to the NRO Savings Bank account. The minimum deposit required varies; in general branches, it’s Rs. 1000, whereas in personal Banking Branches, The minimum total customer account/deposit balance should be Rs. 1 lakh for Metro / Urban areas and Rs. 50,000 for Semi-Urban / Rural areas. The principal and interest amounts are partly repatriable, subject to an overall ceiling of USD 1 million or equivalent in a financial year. Nomination facilities are available, and account holders can obtain loans or overdrafts against their deposits, with premature withdrawals permissible. On maturity, automatic renewal occurs for the same period at the prevailing interest rate unless specific renewal instructions are provided.
- Special Term Deposits (STDR): Rupee deposits with fixed tenures are available, with interest compounded quarterly and paid upon maturity along with the principal amount. The minimum deposit required varies depending on the branch type; in general branches, it’s Rs. 1000. In personal Banking Branches, the minimum customer account/deposit balance should be Rs. 1 lakh for Metro / Urban areas and Rs. 50,000 for Semi-Urban / Rural areas. The principal and interest amounts are partly repatriable, subject to an overall ceiling of USD 1 million or equivalent in a financial year. Nomination facilities are provided, and account holders can avail loans or overdrafts against their deposits, with premature withdrawals permissible. Upon maturity, automatic renewal occurs at the prevailing interest rate for the same period unless specific renewal instructions are provided.
- Recurring Deposits (RD): Regular monthly deposits to build savings over time. You earn interest and can get a loan against your deposit. Premature withdrawal is allowed, but the account won’t automatically renew upon maturity. With a minimum monthly instalment of Rs. 100, this scheme offers compounded interest rates. Additionally, there’s a nomination facility available and the flexibility to avail loans or overdrafts against your deposit.
It is important to note that repatriation of funds from NRO accounts has a yearly limit (USD 1 million or equivalent).
- NRO Salary Account: Features of the NRO Savings Bank Account include all the standard functionalities of a regular NRO Savings Bank Account, such as those detailed in the provided link. Additionally, it offers:
- Waiver of service charges for:
- SMS alerts
- NEFT / RTGS transactions conducted through INB
- Issuance of Multi-city cheque books
- Issuance of Demand Drafts
- Issuance of Debit Cards
- Annual Maintenance of Debit Cards
- Issuance of NRI Family Cards
- 50% waiver on NRI Home Loan processing charges
- Waiver of the requirement for NRI Car Loans, with the condition that the account should be at least three months old with continuous salary credit.
In overview, this account is suitable for depositing India-based current income in Indian Rupees. It can be opened individually or jointly with other NRIs / PIOs / OCIs. The permissible account type is Savings Bank, and funds can be deposited through fresh remittances from overseas or transfers from other NRE / NRO / FCNR(B) accounts. Interest income is subject to tax deduction at source, with rates varying depending on residency and Double Tax Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) arrangements between India and the respective country. Additional benefits are offered on NRI Home Loans and Car Loans, along with the waiver of various service charges.
NRO Account Early Withdrawals and Taxes
Here’s a summary of what happens if you withdraw money from your NRO account before the maturity date:
Penalties:
- Within seven days, You lose all interest earned.
- After seven days: Below Rs. 50 Lakhs: You get a penalty of 0.5% on the interest you would have earned if you kept the money until maturity.
- Between Rs. 50 Lakhs and Rs. 1 Crore: You get a penalty of 1% on the interest.
- Above Rs. 1 Crore: You only earn interest when the money is in the account, minus a 1% penalty.
Taxes:
- Interest earned in your NRO account is taxed at source (TDS) by the Indian government.
- The tax rate depends on the amount of interest earned:
- Below Rs. 1 Crore: 30.90%
- Above Rs. 1 Crore: 34.608%
- You might be eligible for a lower tax rate under a Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and your country of residence.
- To claim the DTAA benefit, you’ll need to submit:
- Tax residency certificate from your home country
- Self-declaration form (https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/download-forms)
- Form No. 10F (https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/download-forms)
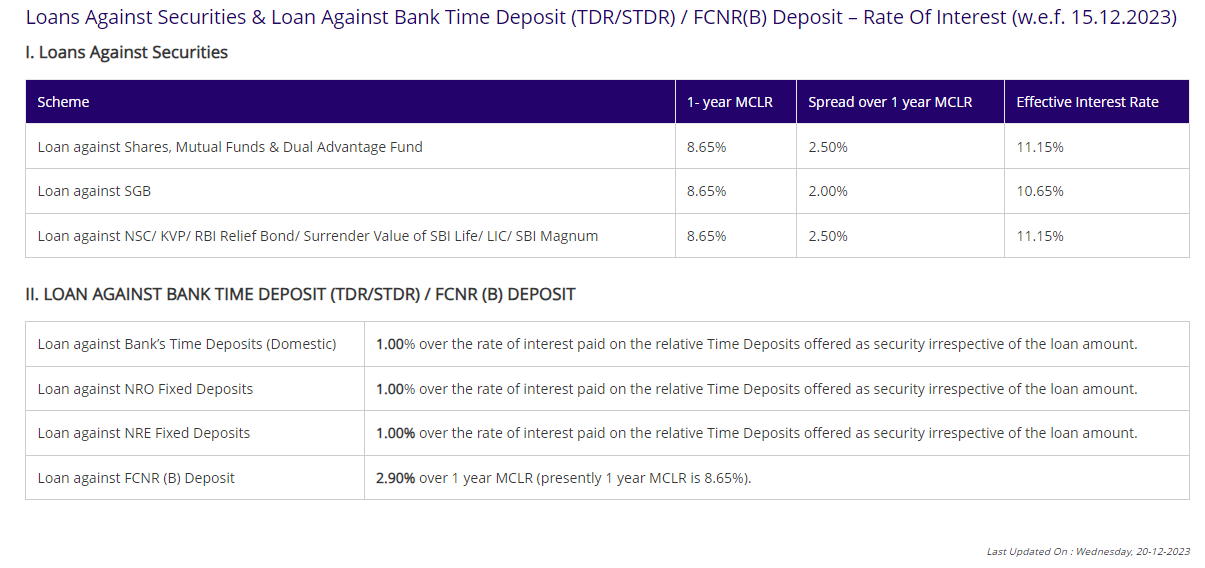
Loans against deposits
Loans can be obtained in Indian rupees against the security of NRO Term Deposit Receipts (TDR), Special Term Deposit Receipts (STDR), or Recurring Deposits (RD). These loans serve various purposes, such as addressing emergency financial needs, funding business activities, making direct investments in India, or acquiring property in India. There’s no requirement to close the deposit to avail the loan prematurely, and it can be obtained at the branch where the deposit is maintained, either as an overdraft or a demand loan. The maximum loan amount is 90% of the face value of the deposit, including accrued interest, with an interest rate typically set at 1.00% above the rate paid on the related deposit used as security. Loans can be utilized for business activities, property acquisition in India, or addressing emergency financial needs but cannot be used for re-lending, agricultural/plantation activities, or real estate investment.
Furthermore, the loan amount cannot be repatriated abroad. Loans can be availed in either Indian Rupees or Foreign Currency against the security of NRE/NRO/FCNR(B) deposits, and they are extended solely to the depositor. Interest is charged monthly for Indian Rupee and Foreign Currency loans. Premature withdrawal of the underlying NRE/FCNR deposit is not allowed. In contrast, premature withdrawal of the NRO deposit is permissible, with the outstanding principal and interest being settled first.
NRO Overdraft Facility
Through internet banking, SBI allows you to create an overdraft account linked to your existing NRO fixed deposit (TDR, STDR, eTDR, or eSTDR). This gives you immediate access to a portion of your deposit funds.
Features of the overdraft facility
- Overdraft Limit: The amount you can borrow depends on your deposit type:
- TDR/eTDR: Up to 75% of the deposit value
- STDR/eSTDR: Up to 90% of the deposit value
- Loan Amount: Minimum Rs. 25,000, Maximum Rs. 5 Crore
- Interest Rate: 1% higher than the interest you earn on your fixed deposit
- Availability: You can apply online between 8 AM and 8 PM IST
- Accessing Funds: Once approved, you can manage your overdraft through Internet banking or use cheques (request a cheque book separately).
Important Points:
- The overdraft tenure is limited by the following:
- The original maturity of your deposit (TDR/STDR)
- Three years (for TDR/TDR)
- 5 years (for STDR/eSTDR)
- Interest on your original deposit continues to be credited as usual.
- Automatic deposit renewal is cancelled if you don’t close the overdraft before maturity.
- You can only close the overdraft account by visiting your home branch (not through internet banking).
Eligibility Criteria for Overdraft Facility
The eligibility criteria for availing loans against fixed deposits include being a customer with NRE/NRO Fixed Deposits (TDR/STDR/eTDR/eSTDR) held solely in the depositor’s name, with a minimum residual period of 6 months. Deposits with joint holders are not considered eligible for the scheme. Additionally, TDR/STDR deposits not opened through Internet banking need to be linked to Internet banking to access this facility.
To create an Overdraft account, follow these steps:
- Log in to your Internet Banking (INB) account.
- Navigate to the ‘e-Fixed Deposit’ tab.
- Click on ‘Overdraft against Fixed Deposit’ from the column on the left-hand side.
- Select the deposit you wish to use as collateral for the overdraft.
- Follow the provided prompts to proceed with the setup of your Overdraft account.
Funds Transfer From NRO To Overseas Account
When transferring funds from an NRO account to an overseas account, you can repatriate up to USD 1 million or its equivalent, after deducting applicable taxes, per financial year, for legitimate purposes, provided all required documents are submitted. You can submit a request letter for the fund transfer via post, courier, or person.
Funds transfer from NRO to NRE / FCNR (B)
Regarding transferring funds from NRO to NRE or FCNR(B) accounts, such transfers are permitted within the overall limit of USD 1 million or equivalent per financial year upon submission of necessary documents as required. You can submit a request letter for this transfer via post, courier, or in person.
(Click here for the standard request letter: https://sbi.co.in/web/nri/accounts/download-forms)
To open an NRO (Non-Resident Ordinary) account, you can follow any of the provided modes.
- Online Application: Click on the provided link to fill out the online account opening application following the mentioned process. (https://oaa.onlinesbi.sbi/oaonri/onlineaccapp.htm)
- Manual Application: Click the provided link to download the account opening application. Please complete it manually and send it with attested copies of proofs and documents selected for KYC to your preferred home branch in India. (https://oaa.onlinesbi.sbi/oaonri/onlineaccapp.htm)
- In-Person Application: Fill out the application form and submit it along with proofs and documents selected for KYC by visiting a State Bank of India (SBI) branch in India or overseas.
Choose the most convenient method to initiate the process of opening an NRO account with SBI.
NRO Tax Saving Scheme
- Tax Benefits: Eligible for tax benefits under section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
- The tenor of Deposits: Term Deposits (TDR/STDR/RD) have only a tenor of 5 years. Premature withdrawal is not permitted.
- Loans: Loans against SBI TSS-NRO deposits are not available. The term deposit cannot be pledged as security for any loan or other funds/assets.
- Eligibility: NRI/PIO/OCI customers with a PAN are eligible. Minors cannot open accounts in their single name but can be second account holders with an adult.
- Permissible Credits: Funds can be transferred from NRO/NRE Savings Bank accounts, fresh remittances from abroad, personal cheques from foreign accounts, and proceeds of foreign currency notes/traveller’s cheques.
- Term Deposits (TDR): Rupee deposits with fixed tenure, with interest paid quarterly. Minimum deposit Rs. 10,000/- and maximum Rs. 150,000/- per financial year. Repatriable, subject to an overall ceiling of USD 1 million per financial year. Nomination facility available.
- Special Term Deposits (STDR): Rupee deposits with interest compounded quarterly, paid on maturity with the principal. Similar terms to TDR apply.
- Tax Implications: Income tax is deducted from interest earned in NRO accounts at the source, with rates varying depending on the interest income. TDS is deducted on a maturity or accrual basis annually. DTAA benefit is available upon submission of required documents.
- Joint Account with Residents: NRI/PIO/OCI customers can open joint NRO accounts with resident relatives on a “Former or Survivor” basis. Permissible relatives include members of a Hindu Undivided Family, spouses, and certain other relationships as prescribed
A financial advisor can provide valuable insights tailored to an individual’s specific financial circumstances and goals. They help navigate through the varied investment opportunities and currency options available within FCNR accounts, ensuring compliance with both Indian and international tax laws. Moreover, advisors can offer strategic guidance on how to maximize returns and minimize financial risks, making the process of managing foreign currency assets more effective and streamlined. Reach out to us at office@primewealth.co.in
This blog is for informational purposes only. The information here does not represent legal advice and should not be used as such. Please confirm the accuracy of any data or content from reliable sources on your own.



